Etiology • Autosomal-dominant trait with high penetrance and variable
expressivity • Mutations in SH3-binding protein on chromosome 4p16.3 • Widespread membranous and endochondral defects in cranio-
facial complex
Clinical Presentation • Chief head and neck manifestations include the following:
expressivity • Mutations in SH3-binding protein on chromosome 4p16.3 • Widespread membranous and endochondral defects in cranio-
facial complex
Clinical Presentation • Chief head and neck manifestations include the following:
• Defective ossification • Wormian bones with calvarial defects • Delayed fontanelle and suture closure
• Variably developed clavicles often a prominent skeletal finding • Long, narrow neck with variably drooped shoulders • Midface deficiency secondary to hypoplasia of facial bones
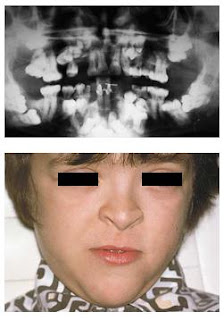
and paranasal sinuses • Ocular hypertelorism • Palate with narrow, high-arched quality • Delayed closure of mandibular symphysis • Multiple unerupted and malpositioned teeth with lack of
cellular cementum • Multiple supernumerary teeth
Diagnosis • Clinical features • Radiographic findings (skull, jaw, chest)
Differential Diagnosis • Achondroplasia • Pyknodysostosis • Hydrocephalus
Treatment • Genetic counseling • For dental abnormalities, treatment options are as follows:
• Early orthodontic intervention • Surgical exposure of unerupted teeth • Extraction of supernumerary teeth
• Surgical correction of jaw deformities • Dental reconstruction
Prognosis • Stability with growth cessation • Dental and oral rehabilitation can proceed as per usual after
surgery (see above) is completed.
Prognosis • Stability with growth cessation • Dental and oral rehabilitation can proceed as per usual after
surgery (see above) is completed.