Diagnosis • Incisional biopsy findings show characteristic EBV nuclear
inclusions in upper-level keratinocytes
Differential Diagnosis • Frictional hyperkeratosis • Lichen planus • Hyperplastic candidiasis
Treatment • None necessary; predisposing condition to be investigated • Can be suppressed with acyclovir for esthetics • Antiviral acyclovir • Podophyllin resin topically
Prognosis • May herald human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease in
vast majority of cases • Also may be present after AIDS is established
inclusions in upper-level keratinocytes
Differential Diagnosis • Frictional hyperkeratosis • Lichen planus • Hyperplastic candidiasis
Treatment • None necessary; predisposing condition to be investigated • Can be suppressed with acyclovir for esthetics • Antiviral acyclovir • Podophyllin resin topically
Prognosis • May herald human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease in
vast majority of cases • Also may be present after AIDS is established
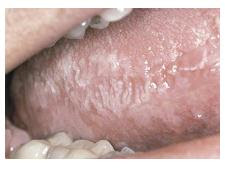 Etiology • Probably due to opportunistic Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection of epithelial cells • Usually in an immunocompromised or immunosuppressed host
Etiology • Probably due to opportunistic Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection of epithelial cells • Usually in an immunocompromised or immunosuppressed hostClinical Presentation • Usually arises on lateral tongue border • Early lesions are fine, white, vertical streaks with an overall
corrugated surface • Later lesions may be thickened to be plaque-like • Extensive lesions can involve dorsum of tongue and buccal
mucosa • May serve as a pre-AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
sign