Etiology • May be primary (idiopathic), secondary to systemic disease, or
familial • Formation of a fibrillar protein deposited in soft tissues and
visceral organs with associated levels of dysfunction
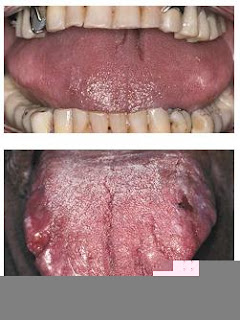
Clinical Presentation • The primary form may produce obvious tongue enlargement
familial • Formation of a fibrillar protein deposited in soft tissues and
visceral organs with associated levels of dysfunction
Clinical Presentation • The primary form may produce obvious tongue enlargement
(macroglossia) and associated purpura, or nodular submucosal alterations.
• The secondary form may be subtle; gingival tissues may contain deposits of amyloid.
Diagnosis • Appearance of tongue • Systemic complaints • Biopsy results: demonstration of amyloid deposits in tissues
(tongue, gingiva)
Differential Diagnosis • Hyalinosis cutis et mucosae (lipoid proteinosis) • Leukemic infiltrate • Lymphangioma • Neurofibromatosis • Hemodialysis-related disorder
Treatment • Directed to underlying cause (secondary) • Localized amyloid tumors may be excised. • Generally symptom related (dialysis, digitalis, depending upon
organ involvement)
Prognosis • When renal impairment exists, transplantation may be necessary.