Salivary Gland Diseases
Mucocele
Etiology • Extravasation type
• Physical-traumatic injury to minor gland excretory duct • Mucus extravasation into periductal soft tissue produces a
local inflammatory response and granulation tissue “encapsulation.”
• Variant • Superficial mucocele • Mucus pool at epithelial–connective tissue junction • Possibly trauma or systemic (hormonal) etiology
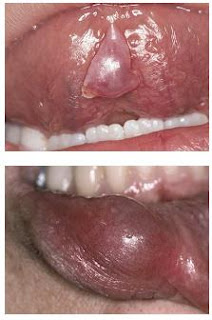
Clinical Presentation • Lower lip most common site; also buccal mucosa, anterior
Mucocele
Etiology • Extravasation type
• Physical-traumatic injury to minor gland excretory duct • Mucus extravasation into periductal soft tissue produces a
local inflammatory response and granulation tissue “encapsulation.”
• Variant • Superficial mucocele • Mucus pool at epithelial–connective tissue junction • Possibly trauma or systemic (hormonal) etiology
Clinical Presentation • Lower lip most common site; also buccal mucosa, anterior
ventral tongue • Painless bluish hue when mucin is near surface • Often waxes and wanes in size
Microscopic Findings • Mucus pool surrounded by granulation tissue • Macrophage and neutrophil response to free mucin • Focal chronic sialadenitis
Diagnosis • Presentation • Microscopic findings
Differential Diagnosis • Hemangioma/varix • Pyogenic granuloma • Salivary neoplasm • Connective tissue neoplasm
Treatment • Excision with associated local minor salivary glands
Prognosis • Occasional recurrence