Tooth Abnormalities
Abrasion
Etiology • Excessive or abnormal wearing of teeth • Commonly associated with use of smokeless tobacco, abrasive
dentifrices, cigars, and pipes, habitual grinding, improper tooth-brushing techniques
• Pathologic wear of teeth associated with abnormal habits or function or consumption of abrasive to coarse diets
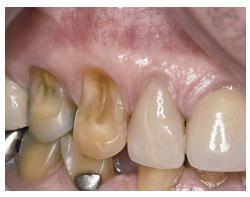
Abrasion
Etiology • Excessive or abnormal wearing of teeth • Commonly associated with use of smokeless tobacco, abrasive
dentifrices, cigars, and pipes, habitual grinding, improper tooth-brushing techniques
• Pathologic wear of teeth associated with abnormal habits or function or consumption of abrasive to coarse diets
• The so-called toothbrush abrasion at the gingival margin may be related to abnormal incisal or occlusal forces producing abfraction injury to enamel at the cementoenamel junction
Clinical Presentation • Causally related appearance includes the following:
• Incisal/occlusal wear related to habit or abrasive diet or substance
• Cervical wear of posterior teeth with chronic, low-grade toothbrush injury
• At occlusal and incisal surfaces, a generalized loss of crown height
• At the cervical margin (cementoenamel junction), horizontal V-shaped to saucerized notches (abfraction injury)
• With exposure of significant root surface, abrasion-related injury, diffuse loss of cementum and dentin
• Pulp canals, containing tertiary dentin, are visible in advanced cases.
Diagnosis • Clinical appearance
Differential Diagnosis • Amelogenesis imperfecta • Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Treatment • Restorative dental techniques • Correction of habits, occlusal force discrepancies
Prognosis • Good
Prognosis • Good