Etiology • A benign epithelial proliferation • HPV is found in most cases; several subtypes have been
identified, especially HPV 6 and 11.
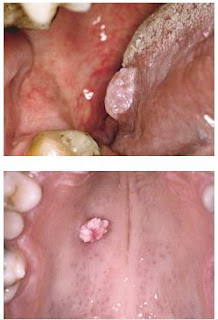
Clinical Presentation • Exophytic, papillary mass, measuring less than 1 cm • Usually pedunculated and soft in texture • White • Usually solitary; may be multiple • Favors soft palate; uvula, tongue, gingiva, buccal mucosa may
also be involved
Microscopic Findings • Epithelial hyperplasia with fibrovascular cores • Papillary projections may be sharp to blunt. • Epithelium may be dysplastic in some lesions from human
immunodeficiency virus–positive patients.
identified, especially HPV 6 and 11.
Clinical Presentation • Exophytic, papillary mass, measuring less than 1 cm • Usually pedunculated and soft in texture • White • Usually solitary; may be multiple • Favors soft palate; uvula, tongue, gingiva, buccal mucosa may
also be involved
Microscopic Findings • Epithelial hyperplasia with fibrovascular cores • Papillary projections may be sharp to blunt. • Epithelium may be dysplastic in some lesions from human
immunodeficiency virus–positive patients.
Diagnosis • Clinical appearance • Biopsy features
Differential Diagnosis • Condyloma acuminatum • Verruca vulgaris • Focal epithelial hyperplasia • Verrucous carcinoma
Treatment • Surgical excision
Prognosis • Low recurrence rate